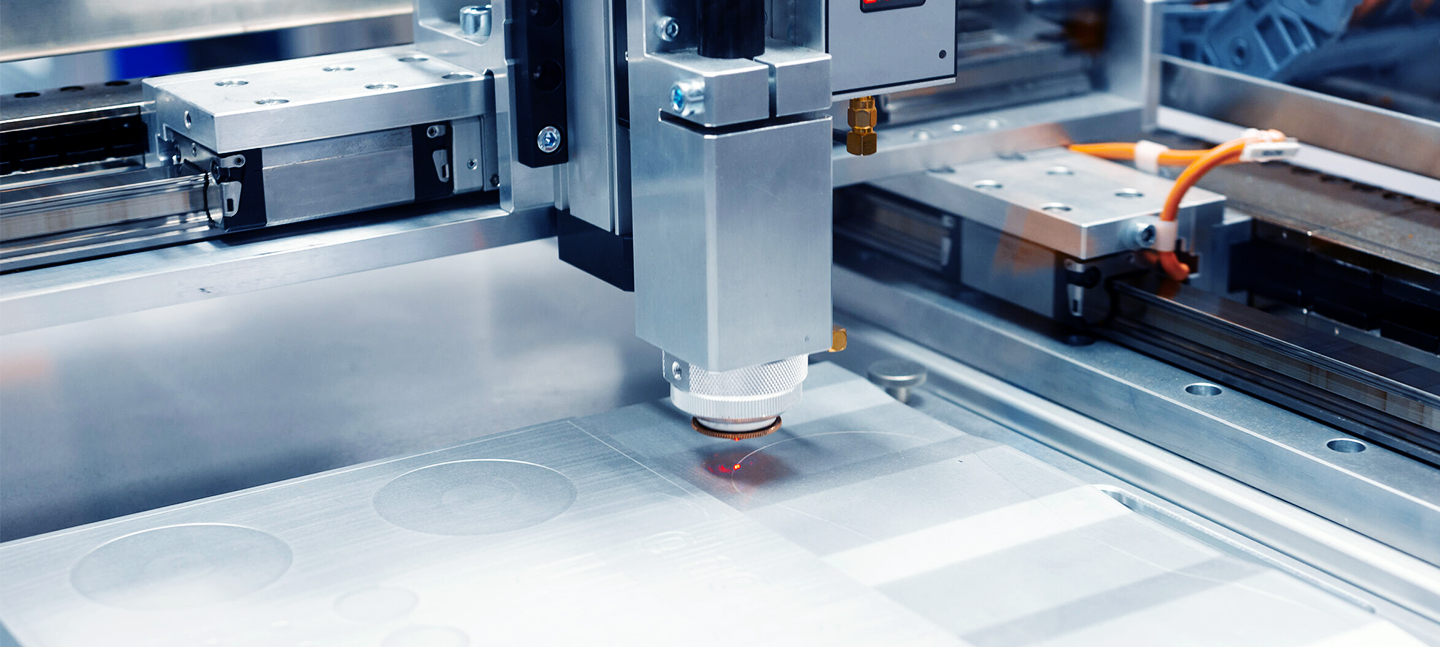
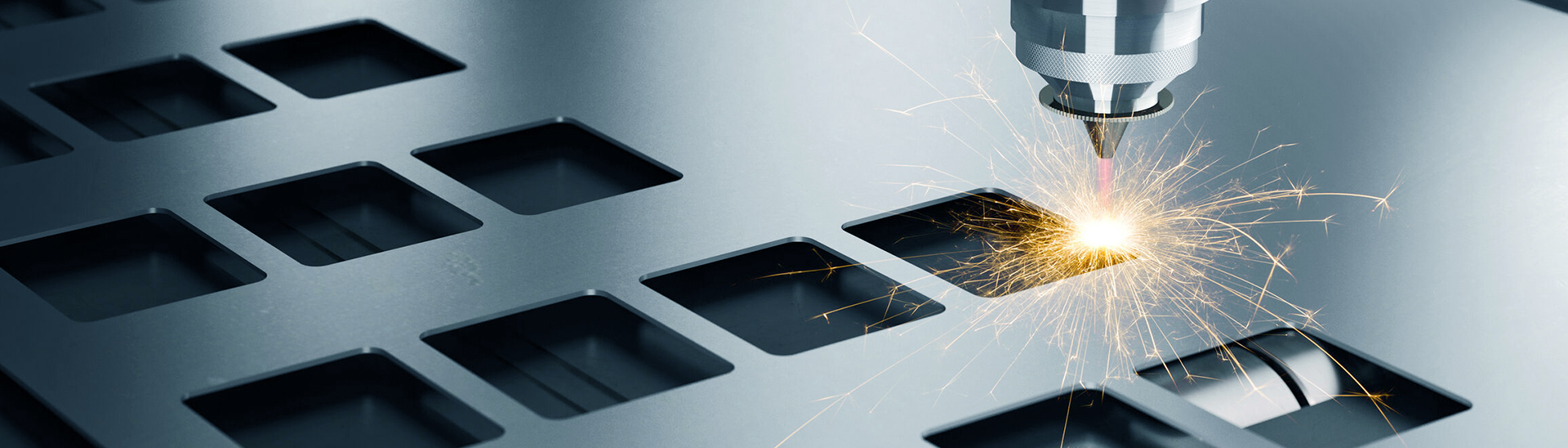
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting aims to convert laser emitted from the laser emitter into high-power-density laser beam through focusing. The laser beam irradiating the surface of work pieces make them reach the melting or boiling point. Meanwhile, high-pressure gas on the same axis with the beam will blow off melted or gasified metals. Accompanied by movement of beam in corresponding to relative position of work pieces, material will form a kerf eventually for the purpose of cutting.
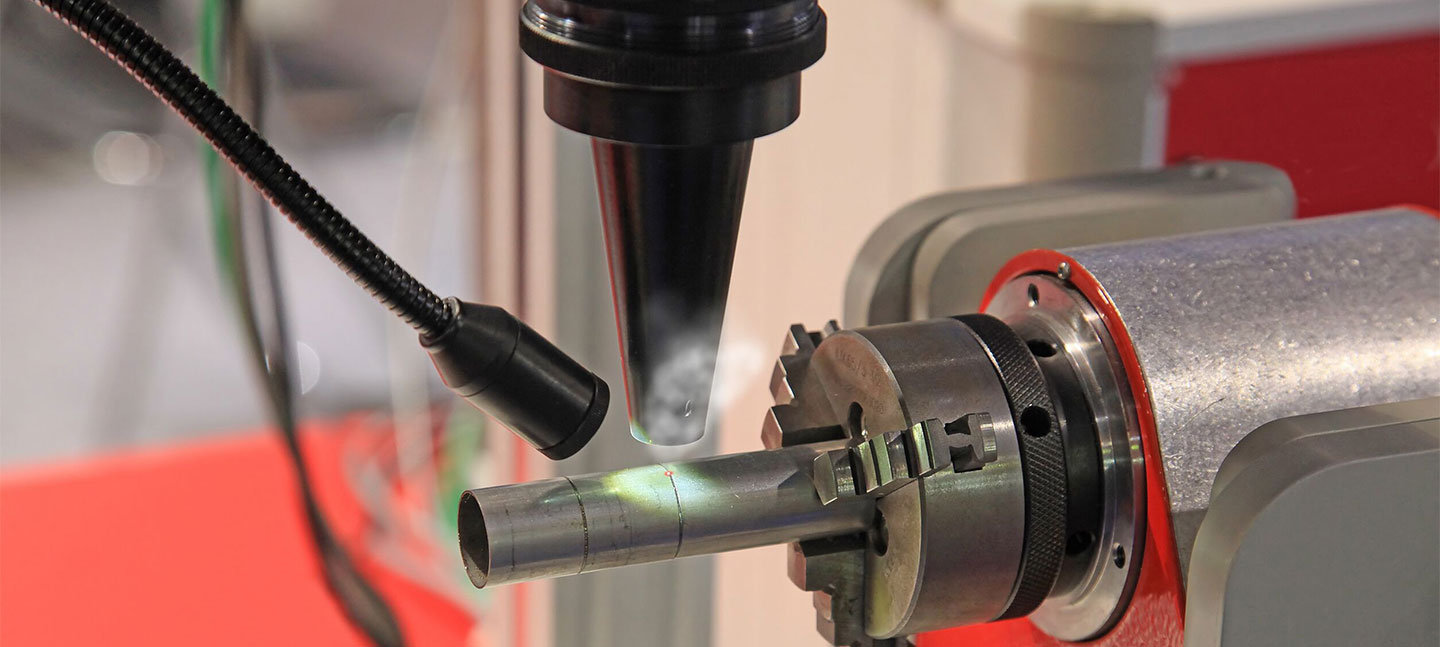

Laser Welding
Laser welding is an efficient precise welding method using high-energy-density laser beam as the heat source. Laser welding represents an important aspect for application of laser material processing technologies. During 1970s, it was mainly used for welding of thin-wall materials and low-speed welding. The welding process is of heat conduction type. In other words, surface of work pieces is heated by laser radiation, and surface heat diffuses internally through heat conduction.
By controlling such parameters as width, energy, peak power and repetitive frequency of laser pulse, work pieces are to be melted to form a specific bath. It has been successfully applied to precise welding of minor and small parts owing to its unique advantages.
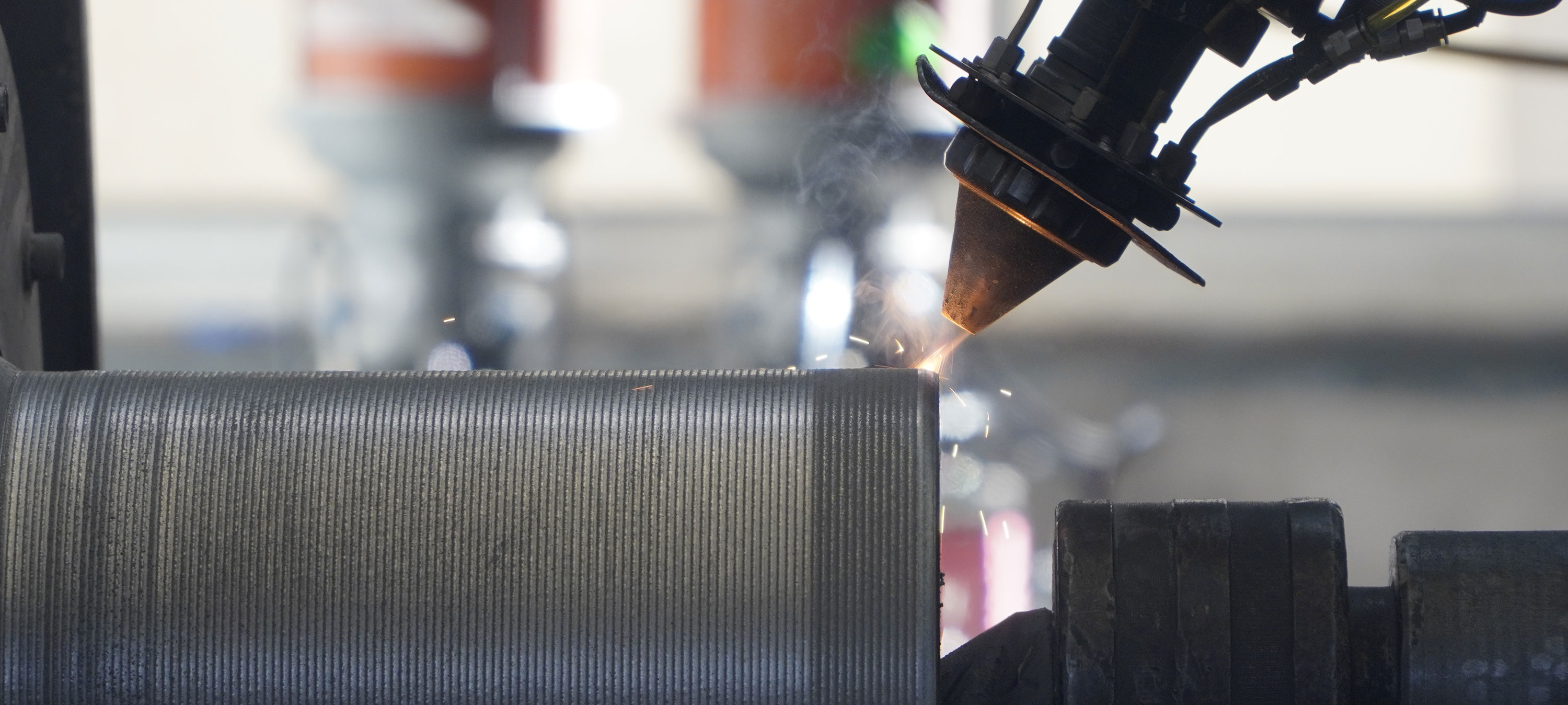

Laser Cladding
Laser cladding is a new surface modification technology. It is expected to form a metallurgically bonded filler cladding by addition of cladding material on the substrate surface, and using high-energy-density laser beam for consolidation with substrate finish.
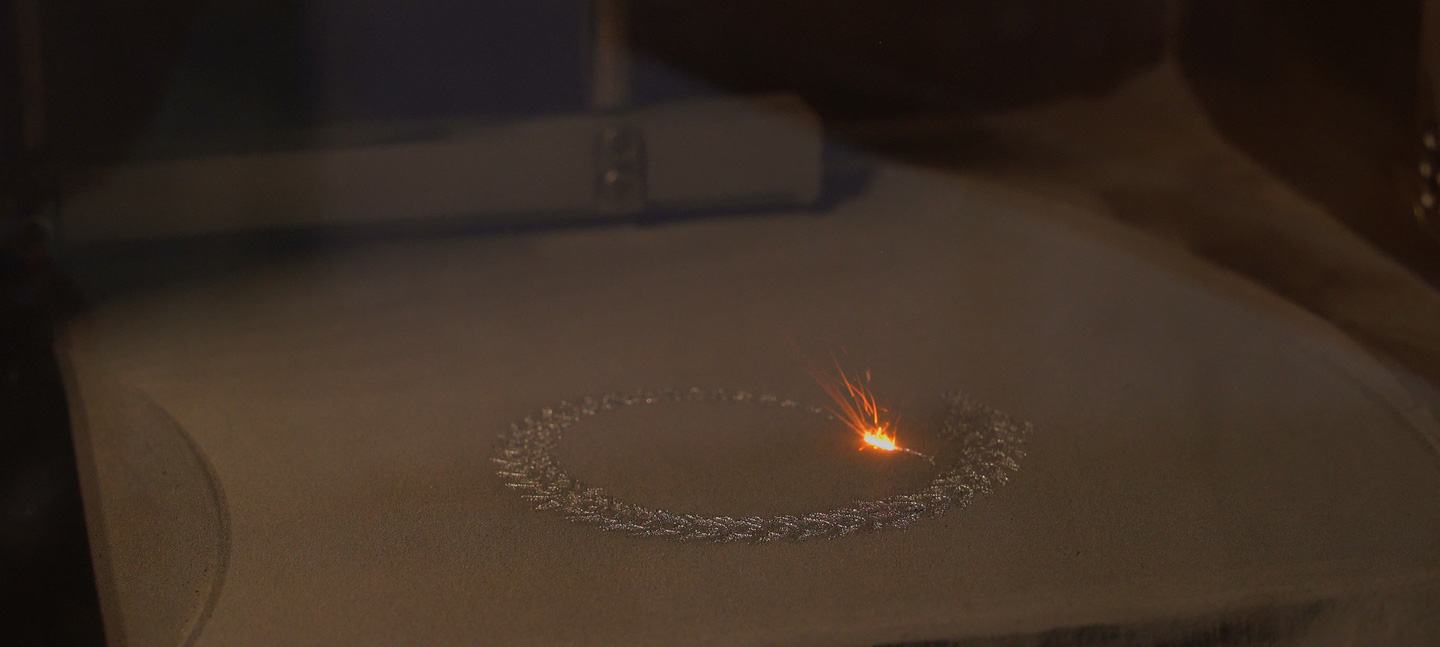
Laser 3D Printing
Laser 3D printing technology integrates computer-aided design, material processing, and forming technologies. Based on digital model files, the software and control system utilize specialized metal materials to manufacture metal components layer by layer through methods such as laser selective melting or deposition. This rapid manufacturing technology is characterized by digitalization, intelligence, and eco-friendliness.